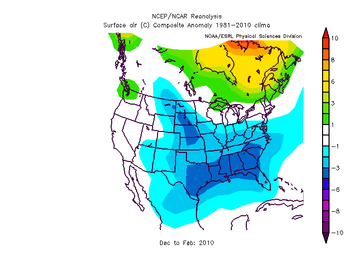
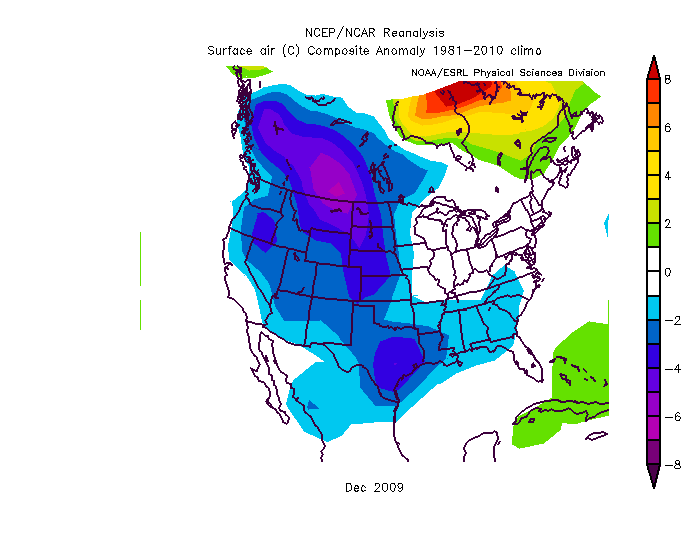
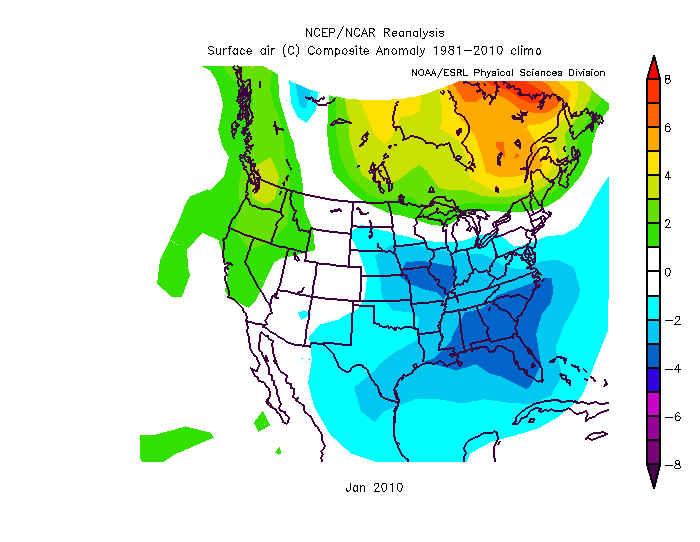
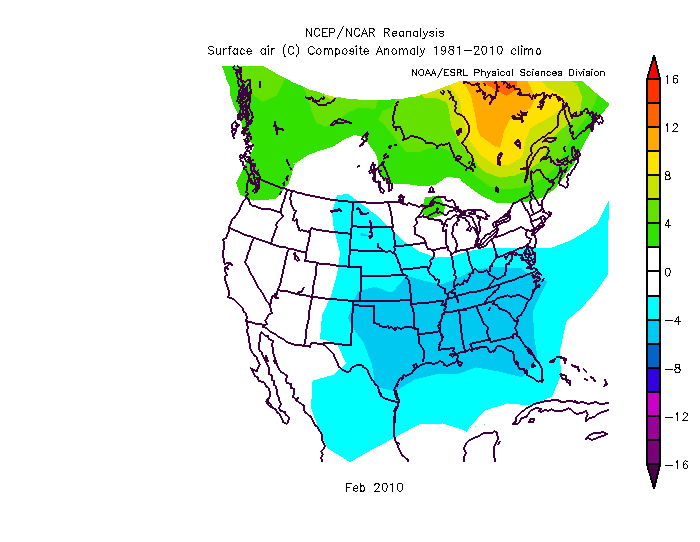
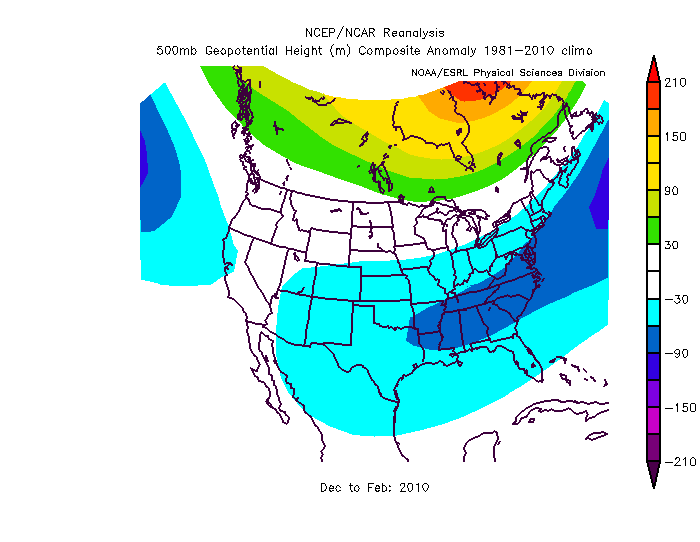
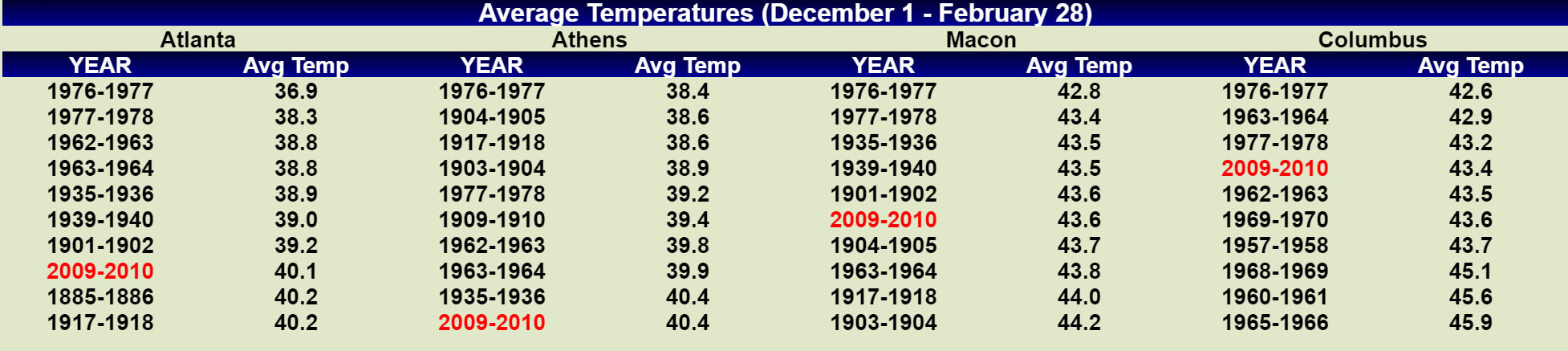
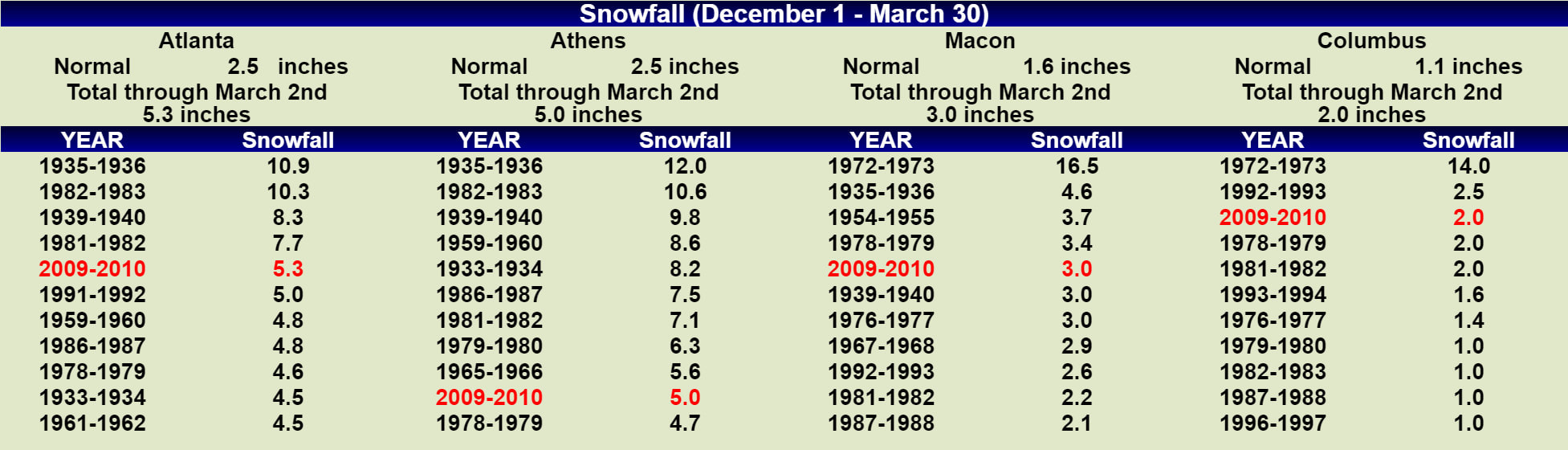
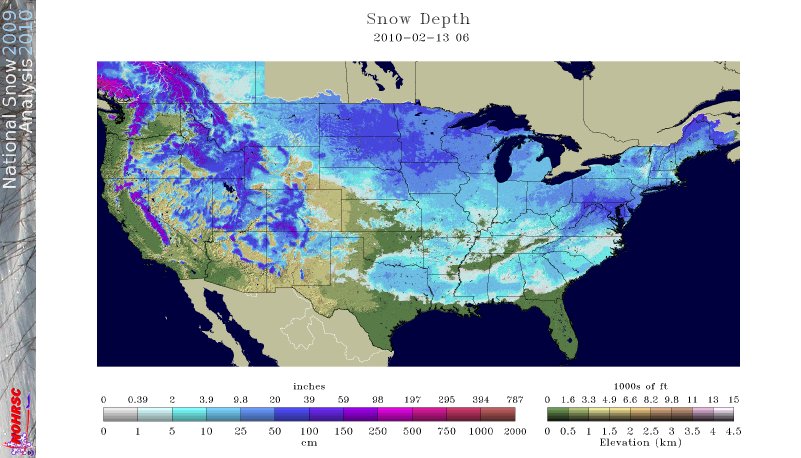
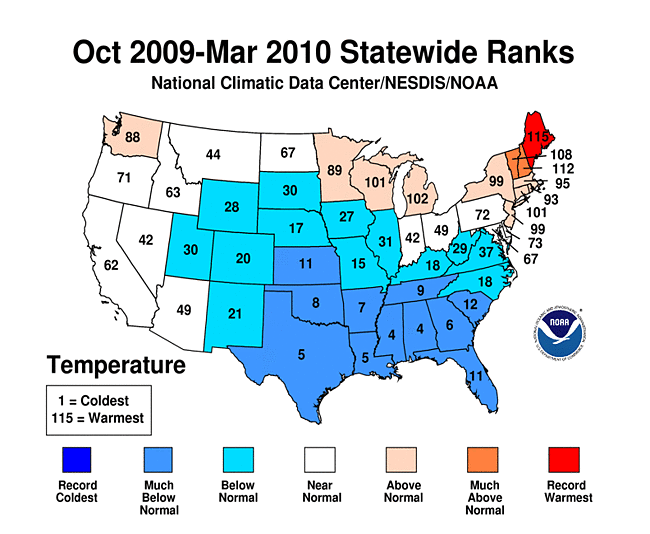
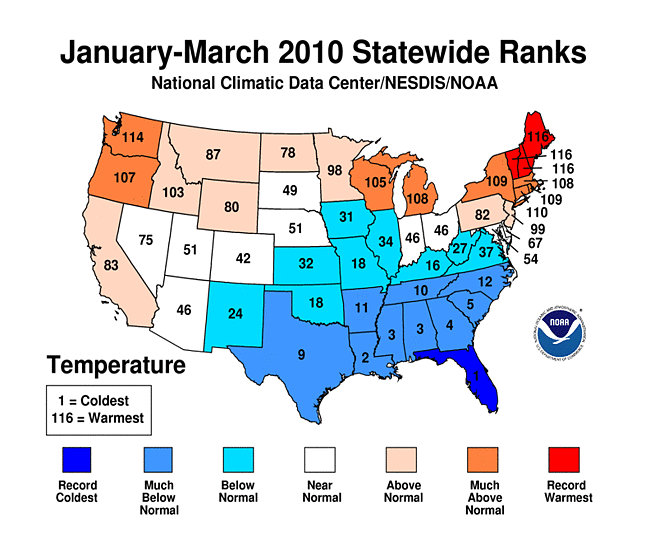
 Dec-Feb Temp Anomalies Dec-Feb Temp Anomalies One of the winters that is an analog for the Weatherbell forecast is the winter of 2009-2010. Since you probably don't remember many of the details, I've brought many of them together here for you to read. My next post will be another analog, 2002-2003. The average temperatures for the December 2009 - February 2010 period were among some of the coldest ever across north and central Georgia. Each of the four climate sites - Atlanta Hartsfield-Jackson International Airport, Athens Ben Epps Airport, Columbus Metropolitan Airport, and Macon/Middle Georgia Regional Airport - saw average temperatures among the ten coldest ever recorded. The average temperatures for Columbus had the 4th coldest average temperature for the winter season, while Macon tied for the 5th coldest, Atlanta was the eighth coldest and Athens tied for the ninth coldest winter season. I broke out the anomalies for each month for that winter, and this is what those looked like. The total snowfall this season at Atlanta breaks top 5 for total snowfall recorded December through March for the period of record. As of midnight Wednesday March 3, the total snowfall for the winter season was 5.3 inches which is now the fifth highest since accurate snow records began in 1929. Additionally... the snow on March 2nd marks the third time measurable snow and the tenth time at least a trace of snow or sleet fell at Atlanta Hartsfield-Jackson International Airport this season. In an average winter season Atlanta typically experiences 4 days of measurable snow and 6 days with a trace or more of snow or sleet A few of my own pictures...These two images were taken on February 11th and 12th, 2010 and on the 12th, there was snow on the ground in all 50 US states. The National Weather Service has a few of the events documented on their website, and here are three events they have listed, but there were more. Click on any image to enlarge it. January 7th, 2010 - Snow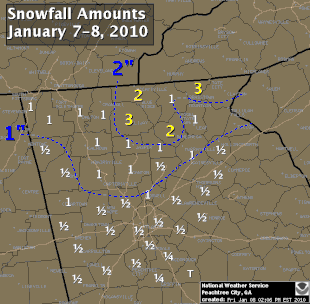 On Thursday, January 7th, a cold front pushed across north and central Georgia, with the combination and timing of cold air and moisture bringing wintry precipitation across the area. Light snow began during the late morning hours. Snow fell across the area through the day and into the early hours of Friday January 8th. The reinforcing cold air behind the front remained across much of the area through the weekend. North and much of central Georgia's temperatures stayed at or below freezing through Sunday. The map to the left shows the snowfall amounts across north and central Georgia. March 2, 2010 Snow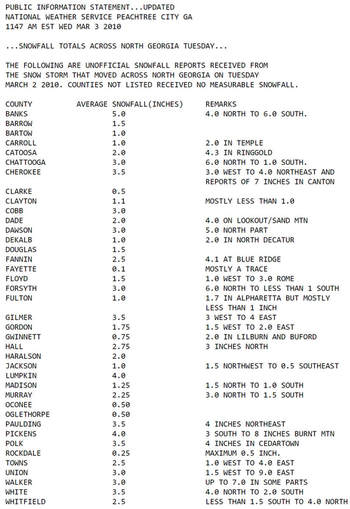 An upper level disturbance traversing the western portion of the United States February 28 and March 1, 2010 helped to develop a surface low along the Texas coast on March 1. This surface low pressure system tracked along the Gulf coast and advected moisture ahead of the system into Georgia from both the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean. By Tuesday, March 2, the surface low moved across southern Georgia and the Florida panhandle and by that afternoon, had moved into the Atlantic Ocean along the Carolina coast. This system brought both rain and snow to the state. Precipitation started as rain and began moving into western Georgia just before midnight on March 2. During the morning hours on March 2 the precipitation continued moving across the state and changed to snow across north Georgia. The snow proceeded to change back to rain during the afternoon and ended across eastern Georgia late in the evening. Snowfall amounts averaged from 2 to 4 inches across north Georgia. However, higher values were reported across northeast Georgia with reports of 9.0 inches in Union county. February 12th, 2010 Snow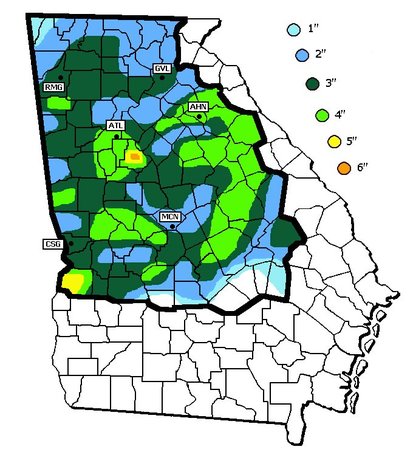 On Friday, February 12th, precipitation associated with a surface low tracking across the Gulf of Mexico and an upper level short wave tracked across much of north and central Georgia. Light snow began over portions of west Georgia around noontime, then spread eastward through the afternoon before tapering off to flurries by mid evening and dissipating by early Saturday morning. Snow and slush on the roadways froze overnight leading to hazardous driving conditions late Friday night into Saturday morning. The map to the left shows the snowfall amounts across north and central Georgia. National Climatic Data Center - Click here for full review of the Winter of 2009-2010The purpose of this special report is to provide documentation, data analysis, and a preliminary understanding of large-scale climate patterns and their effects on regional weather events. In climatological terms, the Cold Season lasts from October through March. The 2009/2010 Cold Season for North America was historically active and powerful. Extreme fluctuations in temperature and precipitation in the mid-latitudes during this period can be attributed to a wide variety of rapidly progressing weather systems. The persistent systems were influenced by larger scale patterns. The strong warm phase of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) helped to alleviate moderate to exceptional drought across the contiguous United States. Meanwhile, the record-setting negative phase of the Arctic Oscillation produced record cold temperatures in the Deep South. During the October–March period, the contiguous U.S. experienced its eighth wettest such period, while the average temperature was below average (36th coolest). The anomalously cold air, coupled with copious amounts of moisture produced historical snowfall amounts that bested monthly and seasonal records across the country. While the overall drought footprint was at its lowest in the last decade, the moisture surplus caused flooding in the Upper Midwest and New England. High amplitude flow patterns helped the cold arctic air remain entrenched for days and weeks, devastating mild climate crops. The extreme winter of 1977/1978 was similar, as a moderate warm phase of ENSO coincided with a strong negative phase of the Arctic Oscillation. The effects of large-scale climate patterns are often influential on regional weather events and when they are extreme and historic in nature, their local effects are profound and far reaching.
The snow cover extent for the contiguous U.S. during the 2009/2010 Cold Season was above average for the season as a whole, but there was significant variation from month to month. The snowy season got off to an early start with several storms impacting the U.S. during October. These storms helped produce the largest average snow extent during any October for the contiguous U.S. in the 42 year satellite record, according to Rutger's University Global Snow Lab. Conversely, November was very quiet with much below average snow cover. The following three months were cold and snowy with the extent being much above average for December (all time snowiest), January (6th snowiest), and February (3rd snowiest). During January, snow and freezing temperatures were reported as far south as central Florida.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
|
OLD NORTH GA WX BLOG


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
